Drinking Water: Groundwater Standards
What are groundwater standards?
About two-thirds of Wisconsin residents use groundwater as their drinking water source. Wisconsin's groundwater standards are levels set in law that limit the amount of harmful substances that can be discharged into the groundwater.
Wisconsin's groundwater standards have two parts:
- Enforcement standard: Level used to establish limits for discharge to groundwater.
- Preventive action limit: Level used to trigger actions to prevent additional contamination.
How are groundwater standards set?
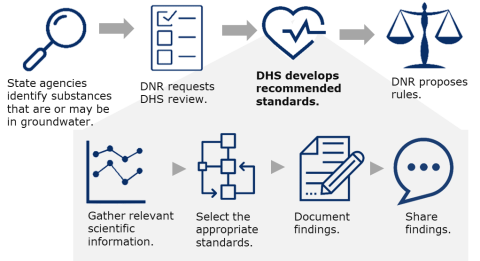
The process for developing groundwater standards is specified in Wis. Stat. ch. 160. The development of groundwater standards occurs in cycles. A groundwater standards cycle begins when state agencies identify substances that are or may be in Wisconsin’s groundwater.
DHS' role is to recommend standards that protect public health.
When requested, we (DHS) gather relevant scientific information, select the appropriate standard based on statutory requirements, and document these findings.
Our Setting Groundwater Standards to Protect Public Health guide, P-02816 (PDF) on this process.
How can I be involved in this process?
When the recommendations are complete, the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR) proposes rules to update or create new standards based on these recommendations. Rulemaking is an extensive process and there are many steps that DNR and the Natural Resources Board must follow during a rulemaking effort. During this time, there are several opportunities for the public to participate in the rulemaking process.
Wisconsin has groundwater standards for which substances?
Since the 1980s, there have been 12 cycles of groundwater standards. Together, this has resulted in approved groundwater standards for more than 130 substances and recommended standards for more than 50 substances.
UPDATE: DHS recently provided the DNR recommendations for six per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as part of the 12th cycle of groundwater standards.
| Substance | Recommended Enforcement Standard | Recommended Preventive Action Limit |
|---|---|---|
| HPFO-DA | 10 ng/L | 1 ng/L |
| PFBS | 2,000 ng/L | 200 ng/L |
| PFHxS | 10 ng/L | 1 ng/L |
| PFNA | 10 ng/L | 1 ng/L |
| PFOA | 4 ng/L | 0.4 ng/L |
| PFOS | 4 ng/L | 0.4 ng/L |
More information on these recommendations is provided in the appropriate sections below.(i)
Acetochlor
The groundwater standards for acetochlor were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =7 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.7 µg/L
Acetochlor is a pesticide used to control weeds in corn. Studies show that exposure to high levels of acetochlor can affect the nose, lungs, liver, kidneys, brain, and reproductive organs.
Acetochlor Ethane Sulfonic Acid and Acetochlor Oxanilic Acid
The groundwater standards for acetochlor ethane sulfonic acid (ESA) and Acetochlor Oxanilic acid (OXA) were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =230 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 46 µg/L
Acetochlor ESA and acetochlor OXA are breakdown products of acetochlor. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of acetochlor ESA and OXA can affect thyroid hormones and body weight.
Acetone
The groundwater standards for acetone were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =9 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 1.8 mg/L
Acetone is used in many industrial processes and consumer products (like nail polish remover). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of acetone can cause kidney, liver, and nerve damage, birth defects, and affect reproductive organs.
Alachlor
The groundwater standards for alachlor were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.2 µg/L
Alachlor is a pesticide used for weed control in a variety of crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of alachlor can affect the kidneys, spleen, blood, and offspring development.
Alachlor ESA
The groundwater standards for alachlor ESA were recommended in Cycle 8 (2006) and adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =20 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 4 µg/L
Alachlor ESA is the breakdown product of alachlor. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of alachlor ESA can affect body weight, blood, and reproduction.
Aldicarb
The groundwater standards for aldicarb were recommended in Cycle 1 (1985).
- Enforcement Standard =10 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 2 µg/L
Aldicarb is a pesticide used to control insects in potatoes. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of aldicarb can affect brain chemistry and cause weight gain.
Aluminum
The groundwater standards for aluminum were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010). In Cycle 10 (2019), DHS recommended that the Preventive Action Limit for aluminum be set at 10% of the enforcement standard due to potential carcinogenic (cancer-causing) effects. However, this change was not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
| Groundwater Standard | Current (Cycle 9) | Recommended (Cycle 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 200 µg/L | 200 µg/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 40 µg/L | 20 µg/L |
Aluminum is a naturally occurring metal that is used in a variety of industrial processes and consume products. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of aluminum can affect reproduction, brain chemistry, and kidney function.
Aminomethylphosphonic Acid
DHS recommended groundwater standards for aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in Cycle 10 (2019).(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =10 mg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 2 mg/L
Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) is a breakdown product of the pesticide glyphosate. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of AMPA can affect the stomach, bladder, and liver and impact development.
Ammonia
The groundwater standards for ammonia were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =9.7 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.97 mg/L
Ammonia is a naturally occurring substance that is common in nature and has many agricultural, industrial, and commercial uses. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of ammonia can affect bones, increase blood pressure, and reduce body weight.
Anthracene
The groundwater standards for anthracene were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =3,000 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 600 µg/L
Anthracene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH). It is used in the production of dyes and to dilute wood preservatives. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing PAHs, studies have shown that swallowing high levels of PAHs can affect the skin, body fluids, and immune system.
Antimony
The groundwater standards for antimony were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =6 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 1.2 µg/L
Antimony is a metal used to make semiconductors and fire-retardant chemicals. Antimony can have beneficial effects when used for medical reasons. However, exposure to high levels of antimony can affect the liver, blood sugar, and the heart.
Arsenic
The groundwater standards for arsenic were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in 2003.
- Enforcement Standard =10 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 1 µg/L
Arsenic is a naturally occurring mineral that is used make glass, electronics, and wood preservatives. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of arsenic can increase the risk of certain types of cancer, affect the skin and nails, and impact the nervous system.
Asbestos
The groundwater standards for asbestos were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =7 million fibers per liter (MFL)
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.7 MFL
Asbestos is a group of minerals that occur naturally in the environment. They have been used in building materials, vehicle components, heat-resistant fabrics, packaging, and coatings. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing asbestos, studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of asbestos may increase the risk for certain types of cancer.
Atrazine
The groundwater standards for atrazine were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 4 (1992). In Cycle 4, the standards were updated to apply to sum of atrazine, 2−chloro−4−amino−6−isopropylamino−s−triazine (deethylatrazine), 2−chloro−4−amino−6−ethylamino−s−triazine (deisopropylatrazine), and 2−chloro−4,6−diamino−s−triazine (diaminoatrazine) combined.
- Enforcement Standard =3 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.3 µg/L
Atrazine is an herbicide used for control of weeds in agricultural crops. Studies have shown that high levels of atrazine can damage the liver, kidney, and heart.
Bacteria (Escherichia coli)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for the bacteria Escherichia coli (E.coli) in Cycle 10 (2019).(iii) The rule to adopt these standards was approved by the Governor on February 2, 2023.
- Enforcement Standard =0 CFU
- Preventive Action Limit = 0 CFU
E. coli are a group of coliform bacteria that are present in the intestinal tract of mammals. They are used to indicate the presence of fecal contamination in groundwater. Exposure to pathogens in drinking water can cause flu-like illness (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fever).
Bacteria (total coliform)
The groundwater standards for bacteria (total coliform) was first adopted in Cycle 1 (1985), updated in Cycle 6 (1995), and reviewed as part of Cycle 10 (2019).(iii) In their rulemaking, DNR changed the groundwater standard type for total coliform from public health to indicator.
Coliforms are a group of bacteria that are naturally present in the environment. They are used to indicate the possible presence of microbial pathogens in groundwater. Pathogens in drinking water can lead to flu-like symptoms (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fever).
Barium
The groundwater standards for barium was first adopted in Cycle 1 (1985), updated in Cycle 5 (1994) and reviewed as part of Cycle 10 (2019). In the Cycle 10 review, DHS did not find any new significant technical information to indicate that a change in the standards was warranted.
- Enforcement Standard =2 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.4 mg/L
Barium is a naturally occurring metal that can get into the environment from power plants and vehicle paints and from drilling mud. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of barium can cause stomach issues and muscle weakness.
Bentazon
The groundwater standards for bentazon were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =300 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 60 µg/L
Bentazon is a pesticide used to control weeds in a variety of crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of bentazon can affect the intestines and blood and alter body weight.
Benzene
The groundwater standards for benzene were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985). The enforcement standard was updated in Cycle 3 (1990) and in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =5 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.5 µg/L
Benzene is used in many industrial processes. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of benzene can affect bone marrow, cause anemia (low red blood cells), rapid heart rate, and impact the nervous system.
Benzo[b]fluoranthene
The groundwater standards for benzo[b]fluoranthene were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =0.2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.02 µg/L
Benzo[b]fluoranthene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) that is formed when fossil fuels, wood, or other organic material is burned. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing PAHs, studies have shown that swallowing high levels of PAHs can affect the skin, body fluids, and immune system.
Benzo[a]pyrene
The groundwater standards for benzo[a]pyrene were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992) and updated in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =0.2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.02 µg/L
Benzo[a]pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) that is formed when fossil fuels, wood, or other organic material is burned. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing PAHs, studies have shown that swallowing high levels of PAHs can affect the skin, body fluids, and immune system.
Beryllium
The groundwater standards for beryllium were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =4 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.4 µg/L
Beryllium is a metal naturally found in mineral rocks, coal, and soil with many industrial uses. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of beryllium can cause ulcers and affect development.
Boron
The groundwater standards for boron were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010). DHS recommended another revision to the standards in Cycle 10 (2019) but these updates were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
| Groundwater Standard | Current (Cycle 9) | Recommended (Cycle 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 1,000 µg/L | 2,000 µg/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 200 µg/L | 400 µg/L |
Boron is commonly found in soil and rocks. Boron compounds have many uses. Small amounts of boron in the diet can have beneficial effects. However, studies have found that exposure to high levels of boron can impact reproduction and development and damage the stomach, intestines, liver, kidneys, and brain.
Bromodichloromethane
The groundwater standards for bromodichloromethane were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990) and updated in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard = 0.6 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.06 µg/L
Bromodichloromethane is formed when drinking water is treated with chlorine to kill germs. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of bromodichloromethane can damage the liver and kidneys, decrease immune response, and increase the risk of miscarriages.
Bromoform
The groundwater standards for bromoform were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement Standard =4.4 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.44 µg/L
Bromoform is formed when drinking water is treated with chlorine to kill germs. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of bromoform can damage the liver, kidneys, and brain.
Bromomethane
The groundwater standards for bromomethane were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =10 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 1 µg/L
Bromomethane is used to make other chemicals and has been used as a pesticide in the past. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing bromomethane, studies have shown that swallowing high levels of bromomethane can damage the stomach.
Butylate
The groundwater standards for butylate were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 8 (2006).
- Enforcement Standard =400 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 80 µg/L
Butylate is an herbicide used control weeds in corn. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of butylate can affect the liver, blood, thyroid, and kidneys, and change body weight.
Cadmium
The groundwater standards for cadmium were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =5 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.5 µg/L
Cadmium is a naturally occurring metal with many industrial uses. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of cadmium can cause stomach irritation and kidney damage.
Carbaryl
The groundwater standards for carbaryl were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =40 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 4 µg/L
Carbaryl is a pesticide used to control a variety of outdoor insects. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of carbaryl cause kidney and liver damage and affect development.
Carbofuran
The groundwater standards for carbofuran were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =40 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 8 µg/L
Carbofuran is a pesticide used to control a variety of outdoor insects. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of carbofuran can affect the nervous system and reproduction.
Carbon disulfide
The groundwater standards for carbon disulfide were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =1000 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 200 µg/L
Carbon disulfide is used to make other industrial chemicals. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels carbon disulfide can damage the liver and heart, affect behavior, and impact reproduction.
Carbon tetrachloride
The groundwater standards for carbon tetrachloride were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =5 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.5 µg/L
Carbon tetrachloride (carbon tet)was used as a cleaning fluid, a component in fire extinguishers, and as a pesticide for grains in the past. It is still used to make other chemicals. Studies have shown exposure to high levels of carbon tetrachloride can impact the nervous system, damage the liver, and affect the digestive system.
Chloramben
The groundwater standards for chloramben were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =150 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 30 µg/L
Chloramben is an herbicide used to control weeds in a variety of crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of chloramben can affect the liver.
Chlorantraniliprole
DHS recommended groundwater standards for chlorantraniliprole in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) = 16 mg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 3.2 mg/L
Chlorantraniliprole is a pesticide used to control insects on a variety of crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of chlorantraniliprole can affect the liver.
Chlordane
The groundwater standards for chlordane were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.2 µg/L
Chlordane was used as a pesticide in the past. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of chlordane can affect the nervous and digestive systems, damage the liver, and impact development.
Chlorodifluoromethane
The groundwater standards for chlorodifluoromethane were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =7 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.7 mg/L
Chlorodifluoromethane is a type of Freon gas. Before the 1970s, it was used as coolant in refrigeration and air conditioning. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of chlorodifluoromethane can affect weight of some organs and impact eye development.
Chloroethane
The groundwater standards for chloroethane were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement Standard =400 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 80 µg/L
Chloroethane is used to make many industrial and consumer products. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of chloroethane can affect development rand coordination and cause stomach irritation.
Chloroform
The groundwater standards for chloroform were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =6 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.6 µg/L
Chloroform is used to make coolants, as pesticide for grains, and as a spot remover in dry-cleaning. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of chloroform can cause liver and kidney tumors.
Chloromethane
The groundwater standards for chloromethane were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =30 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 3 µg/L
Chloromethane (methyl chloride) is given off when certain materials are burned. The biggest health concerns come from breathing chloromethane.
Chlorpyrifos
The groundwater standards for chlorpyrifos were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.4 µg/L
Chlorpyrifos is a pesticide that is used to control variety of insects. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of chlorpyrifos can affect the nervous system and affect behavior.
Chromium (hexavalent)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for hexavalent chromium in Cycle 10 (2019), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =70 ng/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 7 ng/L
Chromium is a naturally occurring metal with many industrial applications. It can exist in many forms in the environment with hexavalent chromium being the most toxic. Studies show that exposure to high levels of hexavalent chromium can affect the immune system, reproduction, development, and liver and kidneys.
Chromium (total)
The groundwater standards for total chromium were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =100 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 10 µg/L
Chromium is a naturally occurring metal that is used in many industrial applications. It can exist in many forms in the environment hexavalent chromium being the most toxic. The standard for total chromium is based on the EPA’s national drinking water standard.
Chrysene
The groundwater standards for chrysene were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =0.2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.02 µg/L
Chrysene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) that is formed when fossil fuels, wood, or other organic material is burned. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing PAHs, studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of some PAHs can affect the skin, body fluids, and immune system.
Clothianidin
DHS recommended groundwater standards for clothianidin in Cycle 10 (2019), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =1,000 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 200 µg/L
Clothianidin is a pesticide used to control a variety of insects. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of clothianidin may affect the liver, kidneys, and blood.
Cobalt
The groundwater standards for cobalt were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999). In Cycle 10 (2019), DHS recommended that the preventive action limit be set at 10% of the enforcement standard due to potential for cobalt to cause birth defects. However, this change was not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
| Groundwater Standard | Current (Cycle 7) | Recommended (Cycle 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 40 µg/L | 40 µg/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 8 µg/L | 4 µg/L |
Cobalt is a naturally occurring element that is used to produce alloys and color glass, ceramics and paints. While small amounts of cobalt are are beneficial to our health, studies have shown that exposure to high levels of cobalt can affect the liver, kidneys, lungs, heart, skin, and may cause birth defects.
Copper
The groundwater standards for copper were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =1,300 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 130 µg/L
Copper is a naturally occurring metal that is used in many industrial and consumer products. Small amounts of copper are needed for good health, but studies have shown that exposure to high levels of copper can cause stomach irritation and damage the liver and kidneys.
Cyanazine
The groundwater standards for cyanazine were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =1 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.1 µg/L
Cyanazine is an herbicide used to control weeds in a variety of crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of cyanazine can cause alter body weight, damage the kidney and livers, affect the blood, and may cause birth defects.
Cyanide
The groundwater standards for free cyanide were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =200 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 40 µg/L
Cyanide is a naturally occurring compound that is used in many industrial processes. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of cyanide may impact the nervous system, thyroid, and reproduction.
Dacthal
The groundwater standards for dacthal were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995) and updated in Cycle 8 (2006). In Cycle 10 (2019), DHS recommended that the standards be applied to the sum of dacthal and the breakdown products, monomethyl tetrachloroterephthalic acid (MTP) and tetrachloroterephthalic acid (TPA). However, these changes were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
| Groundwater Standard | Current (Cycle 8) | Recommended (Cycle 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 70 µg/L (dacthal only) | 70 µg/L (dacthal, MTP, & TPA) |
| Preventive Action Limit | 14 µg/L (dacthal only) | 7 µg/L (dacthal, MTP, & TPA) |
Dacthal is a pesticide used to control a variety of weeds. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dacthal can impact the liver, lungs, kidneys, and thyroid and may increase the risk of cancer. Studies on effects of MTP and TPA are limited.
Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
The groundwater standards for di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992) and updated in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =6 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.6 µg/L
Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) is commonly added to plastics to make them flexible. Studies have shown that high levels of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate can affect sperm and delay sexual maturity.
1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
The groundwater standards for 1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990) and updated in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =0.2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.02 µg/L
1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane (DBCP) is used to make materials that resist burning. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing 1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane, studies have shown that swallowing high levels of 1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane can increase the risk of birth defects.
Dibromochloromethane
The groundwater standards for dibromochloromethane were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =60 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 6 µg/L
Dibromochloromethane can be formed when drinking water is treated with chlorine to kill germs. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dibromochloromethane can damage the liver and kidneys.
1,2-Dibromoethane
The groundwater standards for 1,2-dibromoethane were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =0.05 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.005 µg/L
1,2-Dibromoethane is pesticide used to control insects on a variety of crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,2-dibromoethane can affect sperm and reduce fertility.
Dibutyl phthalate
The groundwater standards for dibutyl phthalate were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =1,000 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 100 µg/L
Dibutyl phthalate is added to plastics to make them more flexible. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dibutyl phthalate exposure can affect the liver and blood.
Dicamba
The groundwater standards for dicamba were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =300 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 60 µg/L
Dicamba is a pesticide used to control weeds. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dicamba can affect body weight.
1,2-Dichlorobenzene
The groundwater standards for 1,2-dichlorobenzene were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =600 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 60 µg/L
1,2-Dichlorobenzene is used to make herbicides. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,2-dichlorobenzene can affect the liver, kidneys, blood, and body weight.
1,3-Dichlorobenzene
The groundwater standards for 1,3-dichlorobenzene were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =600 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 120 µg/L
1,3-Dichlorobenzene is used to make consumer and medical products. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,3-dichlorobenzene can affect the liver, thyroid, and pituitary gland.
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
The groundwater standards for 1,4-dichlorobenzene were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =75 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 15 µg/L
1,4-Dichlorobenzene is used to make mothballs, bathroom deodorants, and resins. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,4-dichlorobenzene can affect the kidneys and blood, cause liver tumors, and may affect nervous system development.
Dichlorodifluoromethane
The groundwater standards for dichlorodifluoromethane were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =1,000 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 200 µg/L
Dichlorodifluoromethane (Freon 12) is a commonly used as a refrigerant and ingredient in insect aerosol bombs. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dichlorodifluoromethane can affect body weight.
1,1-Dichloroethane
The groundwater standards for 1,1-dichloroethane were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and reviewed as part of Cycle 10 (2019).
- Enforcement Standard =850 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 85 µg/L
1,1-Dichloroethane is used to make other chemicals and consumer products. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,1-dichloroethane can cause kidney and liver damage, impact the heart and nervous, affect reproduction and development, and may increase the risk of cancer.
1,2-Dichloroethane
The groundwater standards for 1,2-dichloroethane were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =5 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.5 µg/L
1,2-Dichloroethane is used to make other chemicals, as a solvent for cleaning and degreasing, and to remove lead from gasoline. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,1-dichloroethane can affect the immune and nervous systems, damage the kidneys and liver, and may cause cancer.
1,1-Dichloroethylene
The groundwater standards for 1,1-dichloroethylene were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =7 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.024 µg/L
1,1-Dichloroethylene is used to make fire-retardant materials and food packaging. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,1-dichloroethylene can damage the lungs, liver, and kidneys and may cause tumors.
1,2-Dichloroethylene (cis)
The groundwater standards for 1,2-dichloroethylene (cis) were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =70 µg/L
- Preventive action limit =7 µg/L
1,2-Dichloroethylene (cis) is used to make solvents. While biggest health concerns come from breathing 1,2-dichloroethylene (cis), studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of 1,2-dichloroethylene (cis) can affect the blood and liver.
1,2-Dichloroethylene (trans)
The groundwater standards for 1,2-dichloroethylene (trans) were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988).
- Enforcement Standard =100 µg/L
- Preventive action limit =20 µg/L
1,2-Dichloroethylene (trans) is used to make solvents. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing 1,2-dichloroethylene (trans), studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of 1,2-dichloroethene (trans) can affect the lungs, liver, and heart.
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
The groundwater standards for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985), enforcement standard was updated in Cycle 3 (1990), and the preventive action limit was updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =70 µg/L
- Preventive action limit =7 µg/L
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) is a herbicide that is used to control weeds and invasive species in ponds and lakes. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 2,4-D can damage the kidneys and liver and may cause birth defects.
1,2-Dichloropropane
The groundwater standards for 1,2-dichloropropane were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement Standard =5 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.5 µg/L
1,2-Dichloropropane was used as a solvent in consumer products in the past. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,2-dichloropropane can affect reproduction and damage the liver, kidneys, and brain.
1,3-Dichloropropene
The groundwater standards for 1,3-dichloropropene were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995) and were updated in 2010 (Cycle 9).
- Enforcement Standard =0.4 µg/L
- Preventive action limit =0.04 µg/L
1,3-Dichloropropene is a pesticide used to control roundworms in crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,3-dichloroproprene exposure can damage the stomach, cause skin and eye irritation, and cause anemia (low red blood cells).
Dimethenamid
The groundwater standards for dimethenamid were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =50 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 5 µg/L
Dimethenamid is an herbicide used to control weeds. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dimethenamid can impact the liver, body weight, and reproduction.
Dimethoate
The groundwater standards for dimethoate were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =2 µg/L
- Preventive action limit = 0.4 µg/L
Dimethoate is a pesticide used to control a wide range of insects. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dimethoate can cause stomach and neurological effects.
Dinitrotoluenes
The groundwater standards for 2,4-dinitrotoluene were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement Standard =0.05 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.005 µg/L
The groundwater standards for 2,6-dinitrotoluene were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement Standard =0.05 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.005 µg/L
The groundwater standards for dinitrotoluene (total residues) were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010). These standards apply to the sum of 2,3−, 2,4−, 2,5−, 2,6−, 3,4− and 3,5−dinitrotoluene.
- Enforcement Standard =0.05 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.005 µg/L
Dinitrotoluenes are used to make other chemicals, dyes, and polyurethane foams. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dinitrotoluenes can damage the lungs, liver, and nervous and reproductive systems, and cause anemia (low blood count), headaches, and dizziness.
Dinoseb
The groundwater standards for dinoseb were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and were updated in 1995 (Cycle 6).
- Enforcement Standard =7 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 1.4 µg/L
Dinoseb is a pesticide used to control weeds. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dinoseb can cause neurological effects, weight loss, and damage the thyroid, testes, and intestines.
1,4-Dioxane
The groundwater standards for 1,4-dioxane were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010). In Cycle 10 (2019), DHS recommended revising the standards, but these revisions were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
| Groundwater Standard | Current (Cycle 9) | Recommended (Cycle 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 3 µg/L | 0.35 µg/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 0.3 µg/L | 0.035 µg/L |
1,4-Dioxane is used to make other chemicals. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,4-dioxane can cause affect the liver and kidneys and increase the risk of certain cancers.
Dioxin
The groundwater standards for dioxin (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin) were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990) and were updated in 1995 (Cycle 6).
- Enforcement Standard =0.00003 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.000003 µg/L
Dioxin is formed during the bleaching process at pulp and paper mills and when wastewater is treated with chlorine to kill germs. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of dioxin can cause weight loss, liver damage, weaken the immune system, and lead to birth defects.
4,8-Dioxa-3H-perfluorononanoic acid (DONA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for 4,8-dioxa-3H-perfluorononanoic acid (DONA) in Cycle 11 (2020). However, these standards were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =3 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 0.6 µg/L
4,8-Dioxa-3H-perfluorononanoic acid (DONA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Endrin
The groundwater standards for endrin were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and were updated in 1995 (Cycle 6).
- Enforcement Standard =2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.4 µg/L
Endrin is a pesticide used to control insects, rodents, and birds. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of endrin can affect the nervous system.
S-Ethyl dipropylthiocarbamate
The groundwater standards for S-Ethyl dipropylthiocarbamate (EPTC) were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988).
- Enforcement Standard =250 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 50 µg/L
S-Ethyl dipropylthiocarbamate (EPTC) is an herbicide used to control weeds in a variety of crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of EPTC can affect the brain, heart, nerves, muscles and impact development.
Ethyl ether
The groundwater standards for ethyl ether were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =1000 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 100 µg/L
Ethyl ether is used to make plastics and is found in gasoline engines. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of ethyl ether can damage the liver and affect blood.
Ethylbenzene
The groundwater standards for ethyl ether were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =700 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 140 µg/L
Ethylbenzene is found in fossil fuels and some consumer products. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of ethylbenzene can impact the inner ear.
Ethylene glycol
The groundwater standards for ethylene glycol were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =14 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 2.8 mg/L
Ethylene glycol is found in antifreeze and de-icing solutions. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels ethylene glycol can affect the kidneys, nervous system, lungs, and heart.
Flumetsulam
DHS recommended groundwater standards for flumetsulam in Cycle 11 (2020). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =10 mg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 2 mg/L
Flumetsulam is an herbicide used to control weeds in corn and soybeans. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of flumetsulam can affect the kidneys.
Fluoranthene
The groundwater standards for fluoranthene were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =400 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 80 µg/L
Fluoranthene is a polyaromatic hydrocarbon (PAH). It is released fossil fuels and wood are burned. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing PAHs, studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of some PAHs can affect the skin, body fluids, and immune system.
Fluorene
The groundwater standards for fluorene were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =400 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 80 µg/L
Fluorene is a polyaromatic hydrocarbon (PAH). It is used in resins, dyes, and other chemicals and is released naturally fossil fuels and wood are burned. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing PAHs, studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of some PAHs can affect the skin, body fluids, and immune system.
Fluoride
The groundwater standards for fluoride were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and was updated in cycle 2 (1988) and again in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =4 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.8 mg/L
Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral that is sometimes added to drinking water supplies to prevent dental cavities. Studies have shown that high levels of very high levels of fluoride exposure can cause bones to be brittle and fragile.
Fluorotrichloromethane
The groundwater standards for fluorotrichloromethane were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988).
- Enforcement Standard =3490 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 698 µg/L
Fluorotrichloromethane is a type of Freon gas. Before the 1970s, it was used as coolants or pressurizers in spray can products. The biggest health concerns come from breathing fluorotrichloromethane.
Fomesafen
DHS recommended groundwater standards for fomesafen in Cycle 11 (2020). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =25 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 5 µg/L
Fomesafen is an herbicide used to control weeds in corn and soybeans. Studies have shown that high levels of fomesafen can affect growth, liver function, reproduction, and immune response.
Formaldehyde
The groundwater standards for formaldehyde were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =1000 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 100 µg/L
Formaldehyde is found in a variety of building and consumer products. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing formaldehyde, studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of formaldehyde can reduce body weight, cause stomach ulcers, and damage the liver and kidneys.
Glyphosate
DHS recommended groundwater standards for glyphosate in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these standards were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =10 mg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 1 mg/L
Glyphosate is an herbicide commonly used for weed. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of glyphosate can affect the gastrointestinal system and impact development.
Heptachlor
The groundwater standards for heptachlor were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =0.4 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.04 µg/L
Heptachlor is a pesticide used to control ants. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of heptachlor can cause liver damage, excitability, and decrease fertility.
Heptachlor epoxide
The groundwater standards for heptachlor epoxide were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =0.2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.02 µg/L
Heptachlor epoxide is a breakdown product of the pesticide heptachlor. The standard for heptachlor epoxide is based on the EPA’s national drinking water standard.
Hexachlorobenzene
The groundwater standards for hexachlorobenzene were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =1 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.1 µg/L
Hexachlorobenzene is formed during the production of other chemicals. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of hexachlorobenzene can affect the nervous system and damage the liver, kidney, and thyroid.
n-Hexane
The groundwater standards for n-hexane were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =600 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 120 µg/L
n-Hexane is a chemical made from crude oil with many uses. The biggest health concerns come from breathing n-hexane.
Hexafluoropropylene Oxide Dimer Acid (HFPO-DA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (HFPO-DA) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
DHS has provided the DNR updated recommendations as part of Cycle 12.(i) The updated enforcement standard recommendation is based on EPA's 2024 maximum contaminant level for HPFO-DA and the recommended PAL is set at 10% due to carcinogenic and interactive effects.
| Standard | Previous Recommendations (Cycle 11) | Current Recommendations (Cycle 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 300 ng/L | 10 ng/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 30 ng/L | 1 ng/L |
Hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (HFPO-DA) is also known by the trade name GenX and is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). It can be found in stain repellants, food and other packaging, and fire-fighting foam. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect blood and development and cause kidney and liver damage.
Hexazinone
DHS recommended groundwater standards for hexazinone in Cycle 11 (2020). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =400 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 40 µg/L
Hexazinone is an herbicide used to control weeds. Studies have shown that high levels of hexazinone can affect growth and cause liver damage.
Hydrogen Sulfide
The groundwater standards for hydrogen sulfide were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =30 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 6 µg/L
Hydrogen sulfide is formed naturally and is a common byproduct of industrial processes. The biggest health concerns come from breathing hydrogen sulfide.
Imidacloprid
DHS recommended groundwater standards for imidacloprid in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =0.2 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 0.02 µg/L
Imidacloprid (PDF) is a pesticide that is used to control a variety of insects. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of imidacloprid may cause affect the thyroid and reproduction and cause neurological and glucose regulation problems.
Isoxaflutole and Isoxaflutole Diketonitrile
DHS recommended combined groundwater standards for isoxaflutole and isoxaflutole diketonitrile in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =3 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 0.3 µg/L
Isoxaflutole is an herbicide used to control weeds in corn and soybeans. Isoxaflutole quickly breaks down into isoxaflutole diketonitrile. Studies have shown that high levels can cause liver, thyroid, eye, nerve, muscle problems, and tumor development.
Isoxaflutole Benzoic Acid
DHS recommended groundwater standards for isoxaflutole benzoic acid in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =800 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 160 µg/L
Isoxaflutole benzoic acid is a breakdown product of isoxaflutole. After isoxaflutole turns into isoxaflutole diketonitrile, it more slowly, turns into isoxaflutole benzoic acid. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of isoxaflutole benzoic can affect weight gain and food consumption.
Lead
The groundwater standards for lead were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and were updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =15 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 1.5 µg/L
Lead is a heavy metal found in old paint, leaded gasoline, plumbing materials, and certain household items. There is no safe level of lead exposure. Lead can affect learning, mental health, and increase the risk of diseases later in life.
Lindane
The groundwater standards for lindane were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and were updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =0.2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.02 µg/L
Lindane, also known as gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane, is a pesticide is used in shampoos that treat lice. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of lindane can cause seizures, affect the liver and kidneys, decrease immune response, and impact reproduction.
Manganese
The groundwater standards for manganese were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =300 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 60 µg/L
Manganese is a common element found in minerals, rocks, and soil. Studies have shown that high levels of that manganese can impact the nervous system, affect reproduction, and damage the kidneys. People over the age of 50 and babies less six months are the most sensitive to these effects.
Mercury
The groundwater standards for mercury were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985).
- Enforcement Standard =2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.2 µg/L
Mercury is a naturally occurring metal that is used in many industrial and household products. Studies have shown that high levels of mercury can damage the brain and kidneys and affect development.
Metalaxyl
The groundwater standards for metalaxyl were recommended in Cycle 11 (2020).
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =800 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 160 µg/L
Metalaxyl is a pesticide used to control fungus that grows in water. Studies have shown that high levels of metalaxyl affect growth and cause neurological effects.
Methanol
The groundwater standards for methanol were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =5000 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 1000 µg/L
Methanol (also known as wood alcohol) is used to make some medicines and consumer products. Studies have shown that high levels of methanol affect development and the nervous system.
Methoxychlor
The groundwater standards for methoxychlor were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in 1994 (Cycle 5).
- Enforcement Standard =40 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 4 µg/L
Methoxychlor is a pesticide used to control a variety of insects. Studies have shown that high levels of methoxychlor can affect the nervous system.
Methyl ethyl ketone
The groundwater standards for methyl ethyl ketone were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =4 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.8 mg/L
Methyl ethyl ketone (also known as 2-butanone) is chemical used in paints, glues, and cleaning agents. Studies have shown that high levels of methyl ethyl ketone affect the nervous system.
Methyl isobutyl ketone
The groundwater standards for methyl isobutyl ketone were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =500 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 50 µg/L
Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK), also called isopropylacetone, is a chemical that is used in many consumer products. While the biggest health concerns come from breathing methyl isobutyl ketone, studies have shown that swallowing high levels of methyl isobutyl ketone can cause liver and kidney damage.
Methyl tert-butyl ether
The groundwater standards for methyl tert-butyl ether were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement Standard =60 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 12 µg/L
Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) is a chemical that is added to gasoline so that engines produce less carbon. Studies have shown that high levels of methyl tert-butyl ether can increase the risk of certain types of cancer.
Methylene chloride
The groundwater standards for methylene chloride were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =5 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.5 µg/L
Methylene chloride (also known as dichloromethane) is a chemical used as paint remover, industrial solvent, and grain disinfectant. It can also be formed when drinking water is treated with chlorine to kill germs. While biggest health concerns come from breathing methylene chloride, studies have shown that swallowing high levels of methylene chloride can damage the liver and cause tumors.
Metolachlor
The groundwater standards for metolachlor were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =100 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 10 µg/L
Metolachlor is a pesticide used to treat weeds. Studies have shown that high levels metolachlor can affect the liver, body weight, and development.
Metolachlor Ethane Sulfonic Acid and Metolachlor Oxanilic Acid
The combined groundwater standards for metolachlor ethane sulfonic acid (ESA) and metolachlor oxanilic acid (OXA) were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =1.3 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.26 mg/L
Metolachlor ESA and metolachlor OXA are breakdown products of the pesticide, metolachlor. Studies have shown that high levels of metolachlor ESA and OXA have very little toxicity.
Metribuzin
The groundwater standards for metribuzin were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement standard =70 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 14 µg/L
Metribuzin is a pesticide used to control weeds in crops. Studies have shown that high levels of metribuzin can affect the thyroid, liver, blood, development, and body weight.
Molybdenum
The groundwater standards for molybdenum were adopted in Cycle 8 (2006). In Cycle 10 (2019), DHS recommended revising the standards to be based on information from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). However, the recommended enforcement standard was erroneously calculated to be 10-fold lower than it should have been. In April 2024, DHS withdrew the recommended groundwater standard.
- Enforcement Standard =40 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 8 µg/L
Molybdenum is a common element found in minerals, rocks, and soil. It is used in many industrial processes. Studies have shown that high levels of molybdenum can cause kidney and liver damage and impact reproduction and development.
Monochlorobenzene
The groundwater standards for monochlorobenzene were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement Standard =100 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 20 µg/L
Monochlorobenzene (also known as chlorobenzene) is a chemical used to degrease automobile parts and to make other chemicals. Studies have shown that high levels of monochlorobenzene can damage the liver and kidneys and affect the nervous system.
Naphthalene
The groundwater standards for naphthalene were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992) and updated in Cycle 8 (2006).
- Enforcement Standard =100 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 10 µg/L
Naphthalene is found naturally in crude oil and is used to make many consumer and industrial products. Studies have shown that high levels of naphthalene can cause anemia (low red blood cells), liver and kidney damage, and affect the nervous system.
Nickel
The groundwater standards for nickel were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =100 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 20 µg/L
Nickel is a naturally occurring metal with many uses. Studies have shown that high levels of nickel can affect stomach, blood, and liver.
Nitrate
The groundwater standards for nitrate were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =10 mg/L (as nitrate-nitrogen)(iii)
- Preventive Action Limit = 2 mg/L (as nitrate-nitrogen)(iii)
Nitrate is a naturally occurring molecule that can enter groundwater from fertilizers and animal and human waste. Studies have shown that high levels of nitrate can cause blue baby syndrome, birth defects, and increase the risk of thyroid disease and colon cancer.
(iii)This standard also applies to the sum of nitrate and nitrite.
Nitrite
The groundwater standards for nitrite were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =1 mg/L (as nitrite-nitrogen)
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.2 mg/L (as nitrite-nitrogen)
Nitrite is a naturally occurring molecule that can enter groundwater from fertilizers and animal and human waste. It is also used in food preservation, some medications, and the production of munitions and explosives. The standard for nitrite is based on the EPA’s national drinking water standard.
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
The groundwater standards for n-nitrosodiphenylamine were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =7 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.7 µg/L
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine is a chemical that was used in the past to make rubber. Studies have shown that high levels of that n-nitrosodiphenylamine can cause swelling, bladder, changes in body weight, and increase the risk of bladder cancer.
Pentachlorophenol
The groundwater standards for pentachlorophenol were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =1 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.1 µg/L
Pentachlorophenol is used as a pesticide and wood preservative. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of pentachlorophenol can cause excessive heat, liver damage, and affect immune system.
Perchlorate
The groundwater standards for perchlorate were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =1 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.1 µg/L
Perchlorates are used in explosives, fireworks, rocket motors, and used for making other chemicals. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of perchlorates can cause thyroid damage, anemia (low red blood cells), and affect hormone levels.
Perfluorobutanoic Acid (PFBA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA) in Cycle 11 (2020). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =10 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 2 µg/L
Perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorobutane Sulfonic Acid (PFBS)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
DHS has provided the DNR updated recommendations for PFBS as part of Cycle 12.(i) The updated enforcement standard recommendation is based on EPA's 2022 drinking water health advisory for PFBS and the recommended PAL is set at 10% due to interactive effects.
| Standard | Previous Recommendations (Cycle 11) | Current Recommendations (Cycle 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 450,000 ng/L | 2,000 ng/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 90,000 ng/L | 200 ng/L |
Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDA) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =300 ng/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 60 ng/L
Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorododecanoic acid (PFDoA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorododecanoic acid (PFDoA) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =500 ng/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 100 ng/L
Perfluorododecanoic acid (PFDoA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =150 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 30 µg/L
Perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid (PFHxS)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorohexanesulfonic acid (PFHxS) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
DHS has provided the DNR updated recommendations for PFHxS as part of Cycle 12.(i) The updated enforcement standard recommendation is based on EPA's 2024 maximum contaminant level for PFHxS and the recommended PAL is set at 10% due to carcinogenic and interactive effects.
| Standard | Previous Recommendations (Cycle 11) | Current Recommendations (Cycle 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 40 ng/L | 10 ng/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 4 ng/L | 1 ng/L |
Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid (PFHxS) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
DHS has provided the DNR updated recommendations for PFNA as part of Cycle 12.(i) The updated enforcement standard recommendation is based on EPA's 2024 maximum contaminant level for PFNA and the recommended PAL is set at 10% due to mutagenic and interactive effects.
| Standard | Previous Recommendations (Cycle 11) | Current Recommendations (Cycle 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 30 ng/L | 10 ng/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 3 ng/L | 1 ng/L |
Perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorooctadecanoic Acid (PFODA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorooctadecanoic acid (PFODA) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =400 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 80 µg/L
Perfluorooctadecanoic acid (PFODA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) in Cycle 10 (2019).(iii) In Cycle 11 (2020), DHS updated the standards to apply to the sum of PFOS, PFOA, perfluorooctane sulfonamide (FOSA), n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamide (NEtFOSA), n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoacetic acid (NEtFOSAA), and n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoethanol (NEtFOSE). However, these standards were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
DHS has provided the DNR updated recommendations for PFOS as part of Cycle 12.(i) The updated enforcement standard recommendation is based on EPA's 2024 maximum contaminant level for PFOS and the recommended PAL is set at 10% due to carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic, and interactive effects.
| Standard | Previous Recommendations (Cycle 11) | Current Recommendations (Cycle 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 20 ng/L (sum of PFOS + 5 PFAS) | 4 ng/L (PFOS only)(ii) |
| Preventive Action Limit | 2 ng/L (sum of PFOS + 5 PFAS) | 0.4 ng/L (PFOS only)(ii) |
Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). PFAS have been used in many industrial and consumer products for their grease, heat, and stain resistant properties. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of PFOS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in Cycle 10 (2019).(iii) In Cycle 11 (2020), DHS updated the standards to apply to the sum of PFOA, PFOS, perfluorooctane sulfonamide (FOSA), n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamide (NEtFOSA), n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoacetic acid (NEtFOSAA), and n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoethanol (NEtFOSE). However, these standards were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
DHS has provided the DNR updated recommendations for PFOA as part of Cycle 12.(i) The updated enforcement standard recommendation is based on EPA's 2024 maximum contaminant level for PFOA and the recommended PAL is set at 10% due to carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic, and interactive effects.
| Standard | Previous Recommendations (Cycle 11) | Current Recommendations (Cycle 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 20 ng/L (sum of PFOA + 5 PFAS) | 4 ng/L (PFOA only)(ii) |
| Preventive Action Limit | 2 ng/L (sum of PFOA + 5 PFAS) | 0.4 ng/L (PFOA only)(ii) |
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). PFAS have been used in many industrial and consumer products for their grease, heat, and stain resistant properties. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of PFOA can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluorotetradecanoic acid (PFTeA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluorotetradecanoic acid (PFTeA) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) = 10 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 2 µg/L
Perfluorotetradecanoic acid (PFTeA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Perfluoroundecanoic acid (PFUnA)
DHS recommended groundwater standards for perfluoroundecanoic acid (PFUnA) in Cycle 11 (2020), but they were not adopted into administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) = 3 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 0.6 µg/L
Perfluoroundecanoic acid (PFUnA) is a type of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of some PFAS can affect health - potential effects include increased cholesterol levels, decrease antibody response to certain vaccines, and reduced fertility in women.
Phenol
The groundwater standards for phenol were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =2 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.4 mg/L
Phenol is used to make resins and fibers and as a disinfectant. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of phenol can affect the nervous system.
Picloram
The groundwater standards for picloram were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =500 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 100 µg/L
Picloram is a pesticide used for to control weeds. Studies have shown that high levels of picloram can cause affect the nervous system, liver, and stomach, and cause weight loss.
Polychlorinated Biphenyls
The groundwater standards for polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) were adopted in Cycle 4 (1992).
- Enforcement Standard =0.03 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.003 µg/ L
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a group of more than 200 substances. They have been used as coolants and lubricants in transformers, capacitors, and other electrical equipment. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of PCBs can cause liver damage, affect the immune system, impact reproduction and development, and increase the risk of certain cancers.
Prometon
The groundwater standards for prometon were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999) and revised in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =100 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 20 µg/L
Prometon is a pesticide used to control weeds. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of prometon can affect growth.
Propazine
The groundwater standards for propazine were adopted in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =10 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 2 µg/L
Propazine is a pesticide used to control weeds that can be applied before planting, at planting, and after crop emergence. Animal studies have shown that propazine may cause weight loss and affect the endocrine system, which is a system of glands that produce hormones.
Pyrene
The groundwater standards for pyrene were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =250 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 50 µg/L
Pyrene is used to make dyes, plastics, and pesticides. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of pyrene can affect the liver, kidneys, and blood.
Pyridine
The groundwater standards for pyridine were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =10 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 2 µg/L
Pyridine is used to make a variety of consumer and medical products. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of pyridine can cause liver and kidney damage and skin and eye irritation.
No substances at this time.
Saflufenacil
DHS recommended groundwater standards for saflufenacil in Cycle 11 (2020). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iv)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 11) =460 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 11) = 46 µg/L
Saflufenacil is a pesticide used to control weeds in corn and soybeans. Studies have shown that high levels of saflufenacil affect the blood and spleen and impair development.
Selenium
The groundwater standards for selenium were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and revised in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =50 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 10 µg/L
Selenium is a naturally occurring element with many industrial and consumer uses. Small amounts of selenium are needed for good health, but studies have shown that high levels of selenium can irritate the stomach and lead to neurological problems.
Silver
The groundwater standards for silver were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985).
- Enforcement Standard =50 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 10 µg/L
Silver is a naturally occurring metal is found in a wide range of products. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of silver can cause argyria – a condition in which the skin and other tissues turn a blue-gray color.
Simazine
The groundwater standards for simazine were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycles 2 (1988), 4 (1992), and 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =4 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.4 µg/L
Simazine is a pesticide used to control weeds. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of simazine can affect body weight, thyroid function, impact the blood, and cause tumors.
Strontium
DHS recommended groundwater standards for strontium in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =1,500 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 150 µg/L
Strontium is a mineral that is commonly found in soil, bedrock, and groundwater. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of strontium can affect bone development in babies and young children who have a diet that is low in calcium and protein.
Sulfentrazone
DHS recommended groundwater standards for strontium in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) =1,000 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 100 µg/L
Sulfentrazone is an herbicide used to control weeds. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of sulfentrazone can affect reproduction and development.
Styrene
The groundwater standards for styrene were adopted in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =100 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 10 µg/L
Styrene is used to make plastics and rubber. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of styrene can cause hearing loss, changes to the lining of the nose, and liver damage.
Tertiary butyl alcohol
The groundwater standards for tertiary butyl alcohol were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985).
- Enforcement Standard =12 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 1.2 µg/L
Tertiary butyl alcohol is added to gasoline to make it burn more efficiently. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of tertiary butyl alcohol can affect the kidneys and thyroid and delay development.
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane
The groundwater standards for 1,1,1,2-tetrachloroethane were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985).
- Enforcement Standard =70 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 7 µg/L
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane is used as a solvent and is found in wood stains and varnishes. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,1,1,2-tetrachloroethane can affect the kidneys, liver, and nervous system.
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
The groundwater standards for 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =0.2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.02 µg/L
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane is used to clean and degrease metals and is an ingredient in paints and pesticides. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane can cause liver damage, stomachaches, and dizziness.
Tetrachloroethylene
The groundwater standards for tetrachloroethylene (PCE) were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994). DHS recommended revising the standards to be based on EPA’s latest cancer risk assessment in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these updated standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iii)
| Groundwater Standard | Current (Cycle 5) | Recommended (Cycle 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 5 µg/L | 20 µg/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 0.5 µg/L | 2 µg/L |
Tetrachloroethylene (PCE) is a solvent with many applications including dry cleaning and metal degreasing. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of PCE can liver and kidney damage, affect development, and cause confusion.
Tetrahydrofuran
The groundwater standards for tetrahydrofuran were adopted in Cycle 2 (1988).
- Enforcement Standard =50 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 10 µg/L
Tetrahydrofuran is used to make many industrial and consumer products. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of tetrahydrofuran can damage the kidneys and affect development.
Thallium
The groundwater standards for thallium were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.4 µg/L
Thallium is used to manufacture electronic devices, switches, and closures for semiconductors. Studies have shown that exposures to high levels of thallium can irritate the stomach, damage the nervous system, lungs, heart, liver, and kidneys, and affect reproduction and development.
Thiamethoxam
DHS recommended groundwater standards for thiamethoxam in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10) = 120 µg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 12 µg/L
Thiamethoxam is a pesticide used to control a variety of insects. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of thiamethoxam can affect the blood, liver, and reproduction.
Thiencarbazone-methyl
DHS recommended groundwater standards for thiencarbazone-methyl in Cycle 10 (2019). However, these standards were not adopted in administrative rule.(iii)
- Recommended Enforcement Standard (Cycle 10)= 10 mg/L
- Recommended Preventive Action Limit (Cycle 10) = 2 mg/L
Thiencarbazone-methyl used to control a variety of insects. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of thiencarbazone-methyl can affect the kidney, bladder, and urinary tract.
Toluene
The groundwater standards for toluene adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =800 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 160 µg/L
Toluene occurs naturally in crude oil and is to make paints, lacquers, and glues. The biggest health concerns come breathing from toluene.
Toxaphene
The groundwater standards for toxaphene were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =3 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.3 µg/L
Toxaphene is a mixture of hundreds of different chlorinated compounds used to control insects in crops. The EPA banned all uses of toxaphene in 1990. Studies have shown exposure to high levels of toxaphene can damage the liver, kidneys, alter the immune system, and increase the risk of certain types of cancer.
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
The groundwater standards for 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene were adopted in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =70 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 14 µg/L
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene is used to dissolve materials such as oils, waxes, resins, greases, and rubber. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,2,4-trichhlorobenzene exposure can cause liver and kidney damage.
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
The groundwater standards for 1,1,1-trichloroethane were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985).
- Enforcement Standard =200 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 40 µg/L
1,1,1-Trichloroethane is used as a metal degreaser and dry-cleaning solvent. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,1,1-trichloroethane can cause liver, lung, and brain damage.
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
The groundwater standards for 1,1,2-trichloroethane were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 6 (1995).
- Enforcement Standard =5 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.5 µg/L
1,1,2-Trichloroethane is used as a solvent and can be formed when other chemicals break down in the environment. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,1,2-trichloroethane can affect the stomach, blood, liver, kidneys, and nervous system.
Trichloroethylene
The groundwater standards for trichloroethylene were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 3 (1990). In Cycle 10 (2019), DHS recommended revising the standards to be based on EPA’s latest cancer risk assessment. However, these standards were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
| Groundwater Standard | Current (Cycle 3) | Recommended (Cycle 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 5 µg/L | 0.5 µg/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 0.5 µg/L | 0.05 µg/L |
Trichloroethylene (TCE) is a solvent with many applications including dry cleaning and metal degreasing. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of TCE can affect the kidneys, liver, lung, and immune system and may cause certain heart defects in unborn babies.
2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyporpionic Acid
The groundwater standards for 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyporpionic acid were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 5 (1994).
- Enforcement Standard =50 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 5 µg/L
2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyporpionic acid (2,4,5-TP or Silvex) is a pesticide that was used until 1984 due to concerns about contamination with dioxin. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 2,4,5-TP can affect the liver and cause birth defects.
1,2,3-Trichloropropane
The groundwater standards for 1,2,3-trichloropropane were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999). In Cycle 10 (2019), DHS recommended revising the standards to be based on EPA’s latest cancer risk assessment. However, these standards were not adopted into administrative rule.(iii)
| Groundwater Standard | Current (Cycle 7) | Recommended (Cycle 10) |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement Standard | 60 µg/L | 0.3 µg/L |
| Preventive Action Limit | 12 µg/L | 0.03 µg/L |
1,2,3-Trichloropropane is used to make a range of other chemicals. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of 1,2,3-trichloropropane can cause liver and kidney damage, blood disorders, and stomach irritation.
Trifluralin
The groundwater standards for trifluralin were adopted in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =7.5 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.75 µg/L
Trifluralin is a pesticide used to control weeds in crops. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of trifluralin can cause liver and kidney damage and may increase the risk of certain types of cancer.
Trimethylbenzenes
The combined groundwater standards for 1,2,4- and 1,3,5-trimethylbenzenes were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =480 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 96 µg/L
A mixture of 1,2,4- and 1,3,5-trimethylbenzenes is commonly used as an industrial solvent many applications. While biggest health concerns come from breathing trimethylbenzenes, studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of trimethylbenzenes can affect the liver, blood, and overall health.
Vanadium
The groundwater standards for vanadium were adopted in Cycle 7 (1999).
- Enforcement Standard =30 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 6 µg/L
Vanadium is used in producing steels, ceramics, and superconductive magnets. Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of vanadium can affect red blood cells, increase blood pressure, and cause neurological effects.
Vinyl chloride
The groundwater standards for vinyl chloride were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 3 (1990).
- Enforcement Standard =0.2 µg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.02 µg/L
Vinyl chloride is used to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, wire coatings, vehicle upholstery, and plastic silverware. Studies have shown that high levels of vinyl chloride can affect the nervous and immune systems, decrease bone strength, and increase the risk of some cancers.
Xylenes
The combined groundwater standards for meta−, ortho−, and para−xylene were adopted in Cycle 1 (1985) and updated in Cycle 9 (2010).
- Enforcement Standard =2 mg/L
- Preventive Action Limit = 0.4 mg/L
Xylenes are used as a solvent and a cleaning agent. While biggest health concerns come from xylenes, studies have shown that swallowing large amounts of xylenes can affect the liver and cause neurological effects.
These standards have units of milligrams per liter (mg/L), micrograms per liter (μg/L), nanogram per liter (ng/L), colony forming units (CFU), and million fibers per liter (MFL).
(i) DHS Recommended Public Health Groundwater Quality Standards - Cycle 12 Report, P-03694 (PDF), contains the scientific support documents for HFPO-DA, PFBS, PFHxS, PFNA, PFOA, and PFOS.
(ii) DHS' Cycle 12 groundwater standard recommendations do not include perfluorooctane sulfonamide (FOSA), n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamide (NEtFOSA), n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoacetic acid (NEtFOSAA), and n-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoethanol (NEtFOSE) due to changes in the type and format of available technical information and the specific statutory requirements' of the groundwater standards statutory process for establishing recommendations. Instead, DHS has established established individual drinking water health advisories for each substance. Scientific support documents for these health advisories are available upon request.
(iii) In February 2022, the DNR's Natural Resources Board did not approve the rule containing the Cycle 10 recommended groundwater standards. DHS to evaluate risk associated with drinking the water from a private well or public water system. DHS' Recommended Public Health Groundwater Quality Standards - Cycle 10 Report contains the scientific support documents for each substance reviewed as in this cycle.
(iv) In September 2023, the scope statement for the Cycle 11 rulemaking effort expired. DHS' Recommended Public Health Groundwater Quality Standards - Cycle 11 Report, P-02807 (PDF) contains the scientific support documents for each substance reviewed in this cycle.
Support documents for other cycles are available upon request.
Related topics
DNR's NR 140 Groundwater Quality Standards Update page provides status updates on any rule-making efforts to adopt and revise groundwater water standards.
DNR's groundwater law page has information on the process outlined in Ch. 160 for establishing groundwater standards.