Radon in Child Care
Wisconsin Department of Children and Families (DCF) Wis. Admin. Code § DCF 250.06(2)(n)1.a requires Licensed Family Care Centers and Licensed Group Child Care Centers to test for radon. If radon levels exceed the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Action Level of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L), providers are required to install a radon mitigation system to lower radon levels in their center. Licensed providers submit radon test results to DCF. Note that while this rule applies to licensed (not certified) child care providers only, the Department of Health Services (DHS) strongly recommends that certified family centers also test for radon and mitigate high levels. Administrative Code DCF 250 (Family Child Care) and DCF 251 (Group Child Care) require each licensed provider to:
Step 1: Test for radon
Test for radon within six months before providing care for children.
Test in the lowest level of the building used for at least seven hours per week by children in care. Test for at least 48 hours with the building's windows closed.
You can get a test kit at a reduced cost by contacting your regional Radon Information Center.
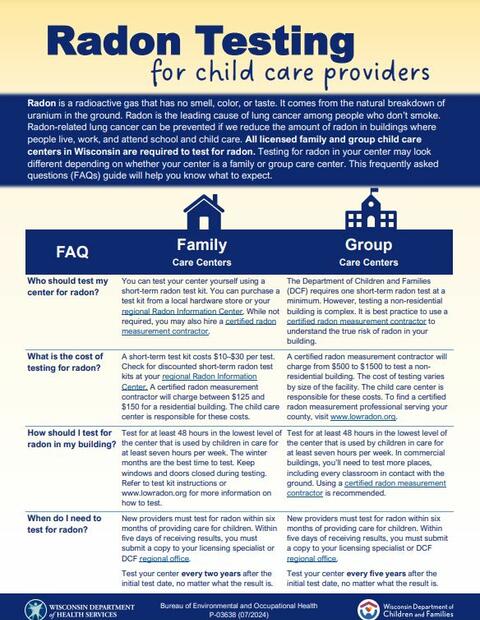
Click flyer for the English version. Also see the Radon Testing flyer for Child Care Providers in Spanish (PDF) and the Radon Testing flyer for Child Care Providers in Hmong (PDF).
Step 2: Send results to DCF
Send a copy of the radon test results to your DCF regional office within five days after receipt.
If results exceed 4 pCi/L, you must notify the parents of children in care.
We offer a template notification letter, P-03638b (PDF) that child care providers are free to use and personalize for their center.
Routine retesting is required.

Click flyer for the English version. Also see the Radon Notification letter for Parents and Guardians in Spanish (PDF) and the Radon Notification Letter for Parents and Guardians in Hmong (PDF).
Step 3: Mitigate if radon test results exceed 4 pCi/L
Hire a certified radon professional to install a radon mitigation system, if test results exceed 4 pCi/L.
After the mitigation system is installed, retest and send results to DCF. Mitigation system installation and retest must be conducted within 12 months of the first radon test with a result over 4 pCi/L.

Click flyer for the English version. Also see the Radon Mitigation flyer for Child Care Providers in Spanish (PDF) and the Radon Mitigation flyer for Child Care Providers in Hmong (PDF).
Why is radon testing in child care centers important?
Protecting children from exposure to high levels of radon can help reduce their long-term risk for developing lung cancer.
Radon is a radioactive gas that you cannot see or smell. It comes from the natural breakdown of uranium and radium in the ground. Radon can enter through a home or building's foundation and build up to high levels in the indoor air. Over time, breathing in high levels of radon can cause lung cancer. It is important to test for radon in places where people spend a lot of time: homes, childcare centers, schools, and workplaces. Children have smaller lungs and faster breathing rates, which increases the dose of their radon exposure. Reducing exposure to radon over the lifespan is key for maintaining health of employees and the future health of children.

Resources
- Fact sheets: Radon testing and mitigation for child care providers, P-03638 (Available in English, Spanish, and Hmong).
- Learn more about radon
- Short video: What is radon?
- Short video: How to test for radon
- Contact your regional Radon Information Center for radon test kits and information
- Funding for radon mitigation systems in child care centers (Payment program A of Child Care Bridge Payments)
- Wis. Admin Code DCF 250 (PDF) (Family Child Care) and Wis. Admin. Code DCF 251 (PDF) (Group Child Care)
- Radon 101 Videos:
Questions?
Experts are available statewide to answer your questions and provide radon test kits. Contact your regional Radon Information Center or call 888-LOW-RADON (888-569-7236). Contact the DCF by finding your regional Child Care Licensing Contact.
