Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
Human metapneumoviruses (HMPV) cause respiratory illness.
They are most commonly diagnosed in young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
To find current levels and transmission of respiratory viruses in Wisconsin, visit Respiratory Virus Data.
Respiratory viruses are primarily spread to others by respiratory droplets and aerosols that travel through the air when an infected person breathes, speaks, sings, coughs, or sneezes.
They can also be spread by contact – either with the infected person (like kissing or shaking hands), or by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your mouth, nose, or eyes.
These viruses can survive on surfaces for many hours.
People infected with HMPV usually show symptoms within three to six days after getting infected. Symptoms may include:
- Runny nose
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
Most people recover within about seven to 10 days. However, people with weakened immune systems, asthma, or respiratory conditions may develop serious illness, such as bronchitis or pneumonia.
There is no specific treatment for illnesses caused by HMPV. Most people will recover on their own. You can relieve your symptoms by:
- Taking pain or fever medications (note: never give aspirin to children)
- Using a room humidifier or taking a hot shower to help ease a sore throat and cough
- Drinking plenty of liquids to stay hydrated
- Staying home and resting
If you are concerned about your symptoms, contact your health care provider.
- Avoid close contact with sick people.
- Wash your hands for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid touching your face (especially mouth, nose, and eyes).
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Disinfect objects and surfaces regularly (like doorknobs, countertops, and light switches).
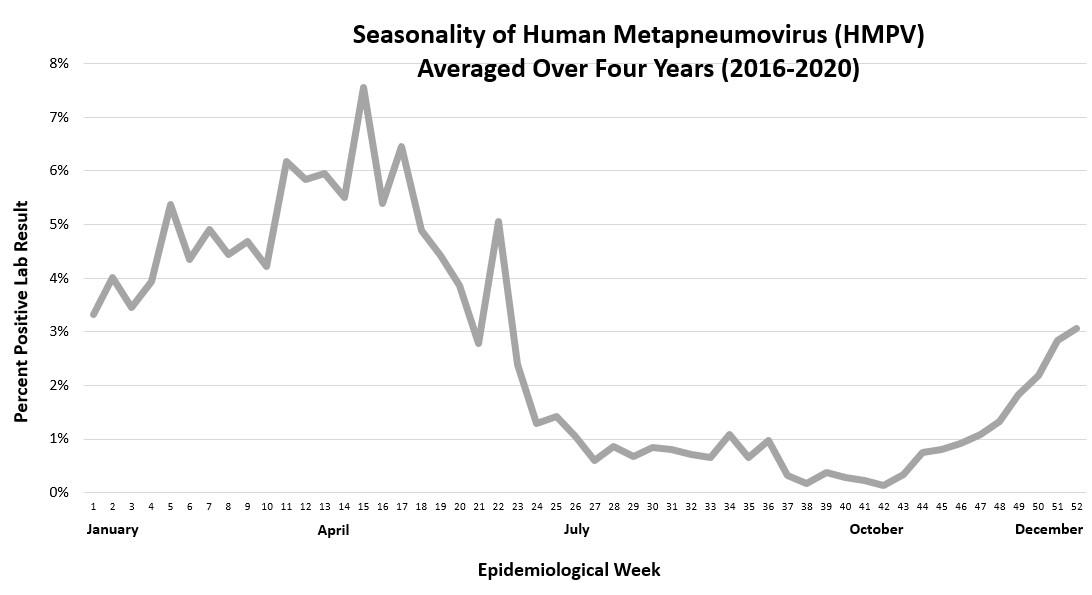
HMVP infections are most common in the late winter and early spring.
- Department of Health Services (DHS): Wash Your Hands!, P-01710: Flyer with instructions on how to properly wash hands.
- DHS: Human Metapneumovirus, P-02195: Flyer with information on human metapneumovirus available in multiple languages.
Individual cases of HMPV are not reportable in Wisconsin. However, clusters of three or more unrelated persons with similar clinical signs and symptoms should be reported to the local health department.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Clinical Features
Questions about human metapneumovirus? Contact us!
Phone: 608-267-9003 | Fax: 608-261-4976