Meningococcal Disease
(Neisseria meningitidis, meningococcal meningitis, meningococcemia)
General information
Invasive meningococcal disease is an acute and serious infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. It can cause sepsis (bloodstream infection), meningitis (inflammation of the tissues that cover the brain and spinal cord), and pneumonia.
- Meningococcal disease fact sheet, P-42072
- Meningitis - CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs) Program - CDC
- Meningitis vaccine recommendations (PDF)
- Information about the Meningococcal vaccine
Those at increased risk for meningococcal disease include:
- Household or close contacts of case patients.
- Patients without a functioning spleen (asplenia).
- People with terminal complement component deficiencies.
- Microbiologists who are routinely exposed to isolates of Neisseria meningitidis.
- Persons traveling to a country where meningococcal disease is epidemic or highly endemic,
- First-year college students who live in residence halls, and military recruits.
- People identified as being at increased risk during an outbreak of meningococcal disease.
Historical and current data for meningococcal disease
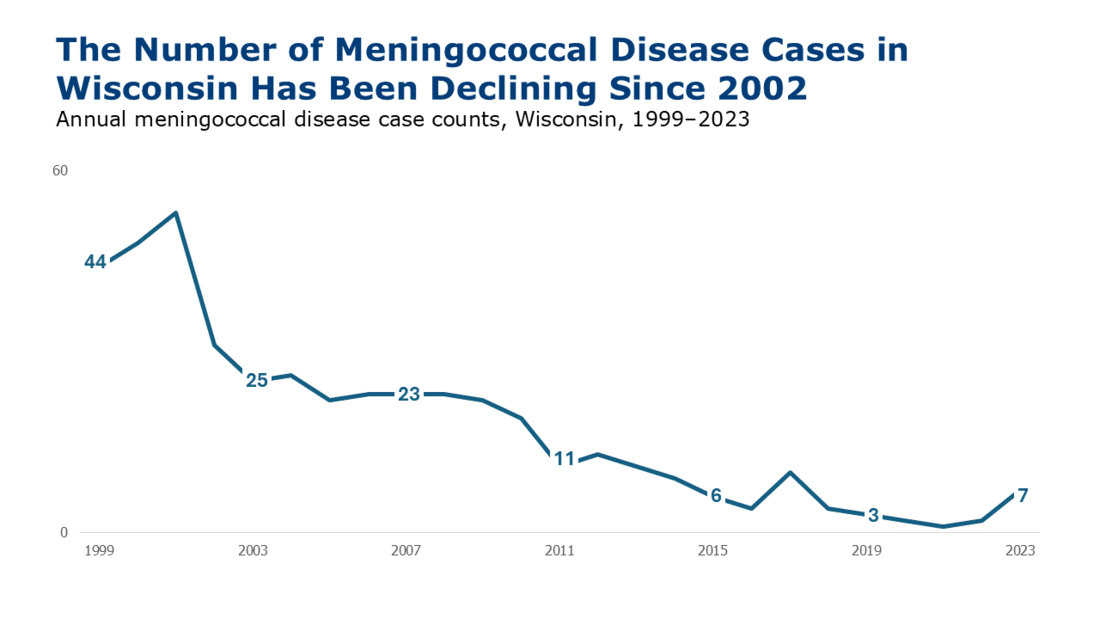
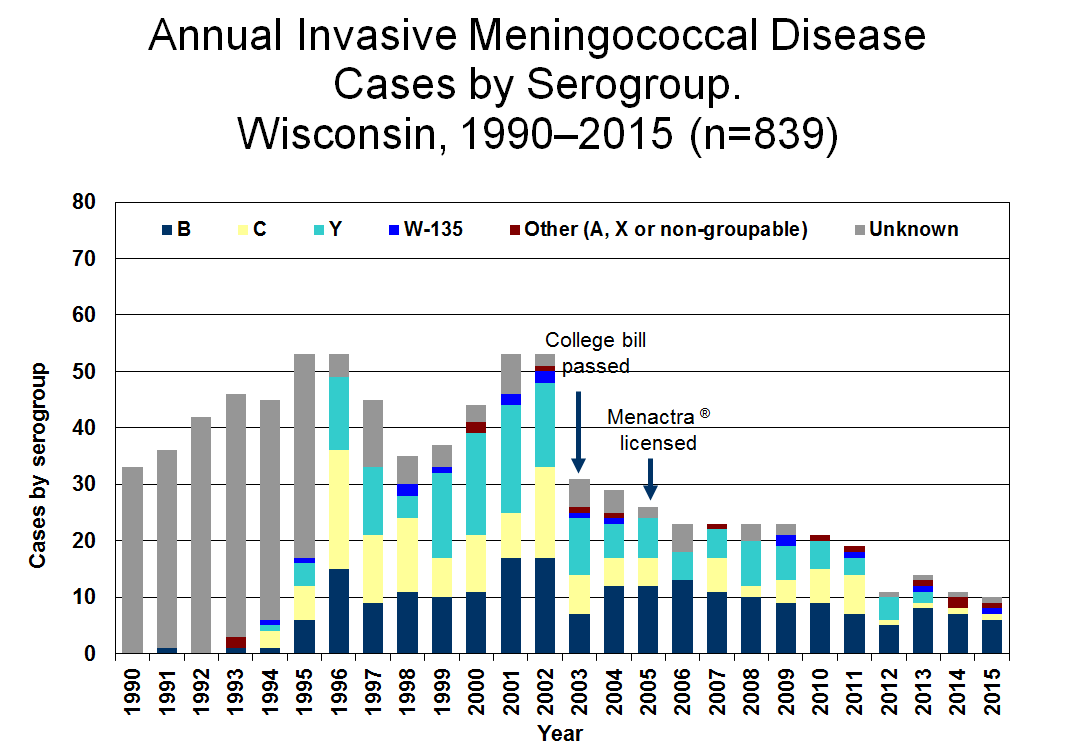
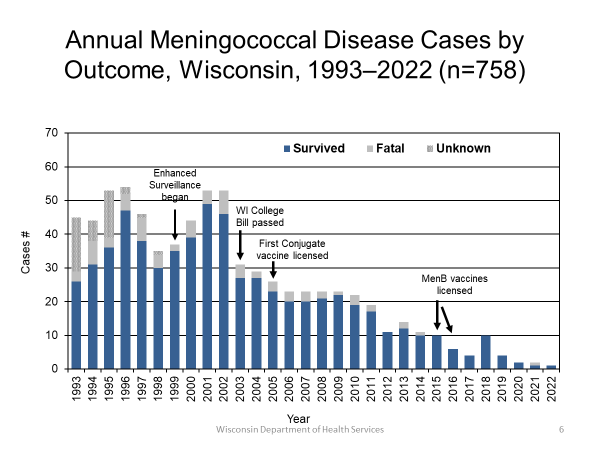
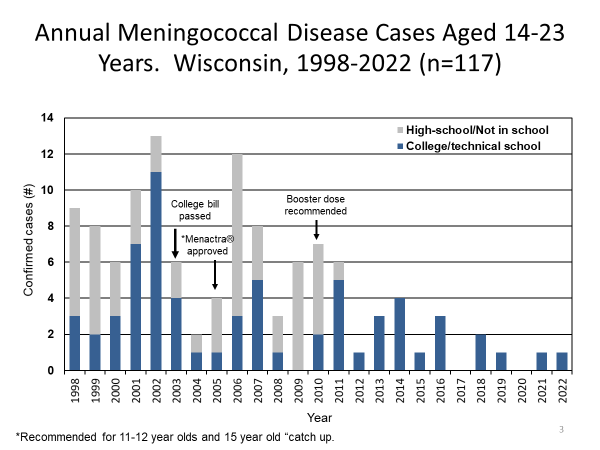
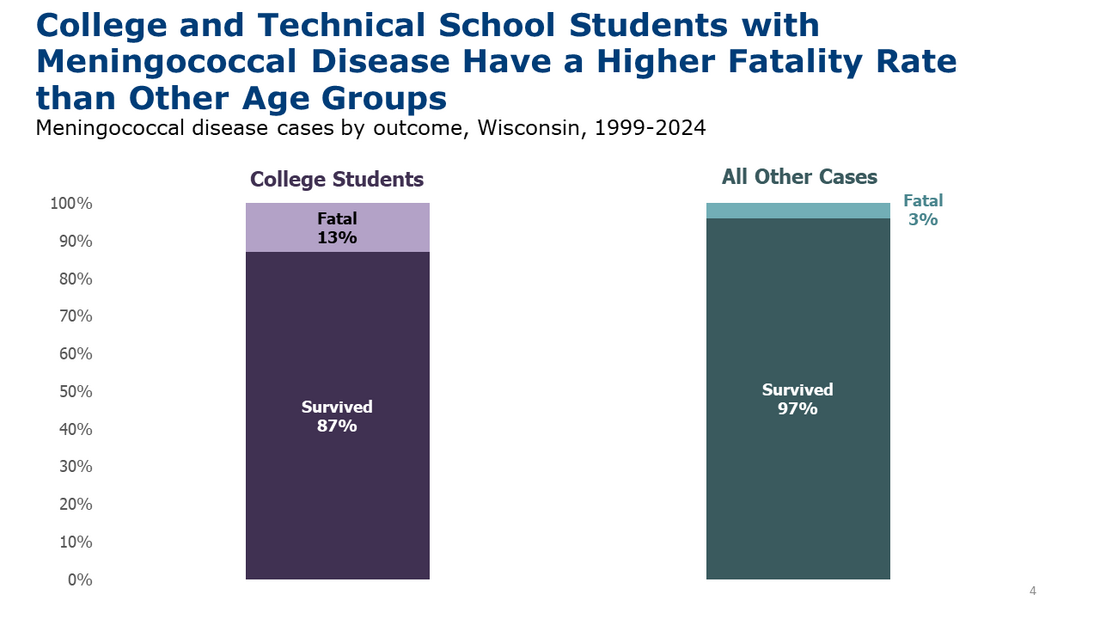
This is a Wisconsin disease surveillance category I disease.
Report immediately by telephone to the patient's local public health department upon identification of a confirmed or suspected case. The local health department shall then notify the state epidemiologist immediately of any confirmed or suspected cases. Submit a case report within 24 hours either electronically through the Wisconsin Electronic Surveillance System (WEDSS), by mail or fax using an Acute and Communicable Disease case report F-44151 (Word), or by other means.
Information on communicable disease reporting
- Case Reporting and Investigation Protocol (EpiNet): Meningococcal disease, P-01975 (PDF) (Neisseria meningitidis)
- Wisconsin Invasive meningococcal disease management protocol P-01626 (PDF)
- Wisconsin Invasive meningococcal disease case investigation flowchart (PDF)
- Wisconsin Invasive meningococcal disease case notification template letter for providers (PDF)
- Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene Clinical Testing Reference Manual
- Information on meningococcal vaccines
- Meningitis vaccine recommendations (PDF)
Questions about Meningococcal Disease? Contact us!
Phone: 608-267-9003 | Fax: 608-261-4976
Wisconsin Local Health Departments – Regional offices – Tribal agencies
