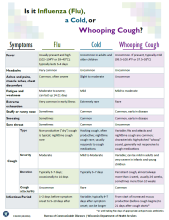
Seasonal Influenza (Flu): Is it the Flu, a Cold, or Whooping Cough?
The myth of the "stomach flu"
Many people use the term "stomach flu" to describe illnesses with nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. These symptoms can be caused by many different viruses, bacteria, or even parasites. The "flu" is a term that generally refers to influenza. While vomiting, diarrhea, and being nauseous or "sick to your stomach" can sometimes be related to the flu, particularly in children, these problems are rarely the main symptoms of influenza. The flu is a respiratory disease and not a stomach or intestinal disease.
Is it the flu, a cold, or whooping cough?
The flu (influenza), colds (viral upper respiratory infections), and whooping cough (pertussis) are highly contagious and, in the initial stages, might seem alike. Check the following table for a comparison of the symptoms for each illness.
Check out the downloadable version of our Is it influenza, cold, or pertussis? (PDF).
| Symptom | Flu | Cold | Whooping Cough |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | Usually present and high (102-104°F or 39-40°C); typically lasts 3-4 days | Uncommon in adults and older children | Uncommon. If present, typically mild (99.5-100.4°F or 37.5-38°C) |
| Headache | Very common | Uncommon | Uncommon |
| Aches and pains, muscle aches, chest discomfort | Common, often severe | Slight to moderate | Uncommon |
| Fatigue and weakness | Moderate to severe; can last up to 14-21 days | Mild | Mild to moderate |
| Extreme exhaustion | Very common early in illness | Extremely rare | Rare |
| Stuffy or runny nose | Sometimes | Common | Common, early in the disease |
| Sneezing | Sometimes | Common | Common, early in the disease |
| Sore throat | Sometimes | Common | Uncommon |
| Type of cough | Non-productive ("dry") cough is typical; nighttime cough rare | Hacking cough, often productive; nighttime cough rare; usually responds to cough medications | Variable; fits and attacks and nighttime cough are common; characteristic high-pitched "whoop" sound, generally not responsive to cough medications |
| Severity of cough | Moderate | Mild to moderate | Variable; can be mild in adults and very severe in infants and young children |
| Length of cough | Typically 3-7 days; occasionally to 14 days | Typically 3-7 days | Persistent cough, almost always >1 week, usually 2-6 weeks, sometimes 10+ weeks |
| Cough attacks/fits | Uncommon | Rare | Common |
| When can you spread the illness to others? | 1-2 days before symptoms appear to 5-10 days after | Variable; typically 4-7 days after symptoms appear; can be longer | From start of increased mucus production (before cough) to 21 days after cough starts* |
* or until taking five days of appropriate anti-pertussis antibiotics.
Helpful links
- Influenza (Flu) Home: DHS flu homepage with information and resources.
- Wisconsin Local Health Departments: Contact information for local public health departments in the state.